The decision between term life insurance and permanent life insurance is a crucial one for individuals seeking financial security for their loved ones. While both options provide coverage in the event of death, they differ significantly in their structure, costs, and benefits. Understanding the nuances of each type is essential for making an informed choice that aligns with your specific needs and financial goals.
This comprehensive guide will delve into the intricacies of term life insurance and permanent life insurance, examining their key features, advantages, and disadvantages. We’ll explore the factors that influence the cost of each type, analyze the coverage needs of different life stages, and shed light on the investment and tax considerations involved. By the end of this article, you’ll have a clear understanding of which type of life insurance is best suited for your unique circumstances.
Life Insurance: Term vs. Permanent
Life insurance is a vital financial tool that provides financial protection for your loved ones in the event of your death. It helps ensure that your family can maintain their standard of living and cover expenses like mortgage payments, debts, and living costs. When choosing life insurance, you have two primary options: term life insurance and permanent life insurance. These options differ significantly in their features, benefits, and costs, making it crucial to understand their nuances before making a decision.
Term Life Insurance vs. Permanent Life Insurance
The primary difference between term life insurance and permanent life insurance lies in their coverage duration and cash value accumulation. Term life insurance provides coverage for a specific period, typically 10, 20, or 30 years. It offers a lower premium than permanent life insurance but does not accumulate cash value. Once the term expires, you can renew the policy, but premiums may increase. Permanent life insurance, on the other hand, provides coverage for your entire life, and it accumulates cash value that you can borrow against or withdraw. However, it comes with higher premiums than term life insurance.
Factors to Consider When Choosing
Several factors can influence your decision between term life insurance and permanent life insurance.
- Your financial situation: If you are on a tight budget, term life insurance might be more suitable as it offers lower premiums. Permanent life insurance can be expensive, especially if you have a large death benefit.
- Your age and health: Younger and healthier individuals generally pay lower premiums for both term and permanent life insurance.
- Your need for cash value: If you need access to cash value for investments or emergencies, permanent life insurance is a better option.
- Your coverage needs: If you need coverage for a specific period, such as while your children are young, term life insurance might be sufficient. However, if you need lifelong coverage, permanent life insurance is a better choice.
Term Life Insurance

Term life insurance is a type of life insurance that provides coverage for a specific period, typically ranging from 10 to 30 years. It is designed to provide financial protection to your beneficiaries in the event of your death during the policy term.
Duration of Term Life Insurance
Term life insurance policies are available for various durations, with common options including 10, 20, and 30 years. The policy term reflects the period for which coverage is in effect. For example, a 20-year term life insurance policy provides coverage for 20 years from the policy’s inception. At the end of the term, the policy expires, and no further coverage is provided.
Death Benefit
The death benefit is the lump-sum payment made to your beneficiaries upon your death during the policy term. The amount of the death benefit is determined at the time of policy purchase and remains fixed throughout the policy’s duration. This benefit is intended to help your beneficiaries cover expenses such as funeral costs, outstanding debts, and living expenses.
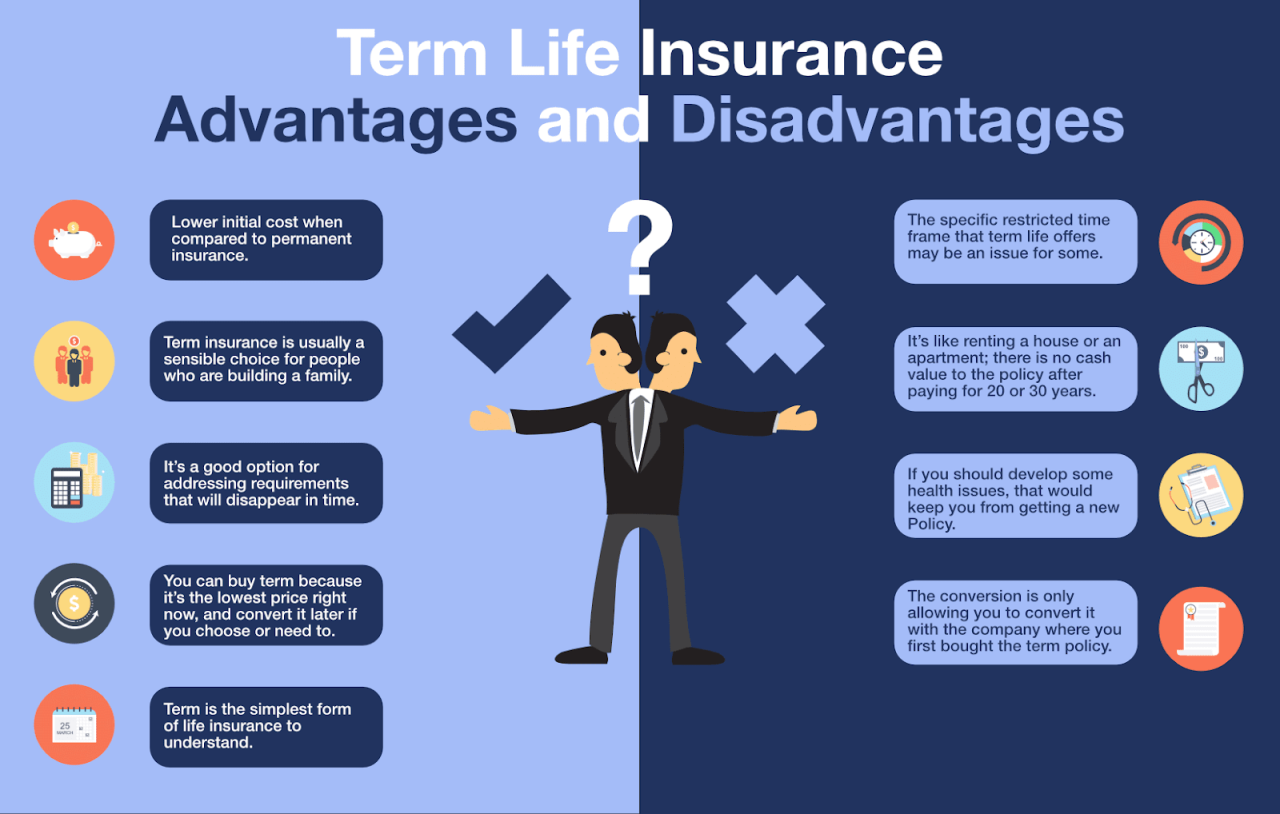
Advantages of Term Life Insurance
Term life insurance offers several advantages, making it an attractive option for many individuals.
- Affordability: Term life insurance is generally more affordable than permanent life insurance, as it only provides coverage for a specific period. This makes it an accessible option for individuals with limited budgets.
- Simplicity: Term life insurance policies are typically straightforward and easy to understand. They focus on providing coverage for a specific period, without the complexities of cash value accumulation found in permanent life insurance.
Disadvantages of Term Life Insurance
While term life insurance offers advantages, it also has some disadvantages that should be considered.
- Limited Coverage: Term life insurance only provides coverage for the specified policy term. Once the term expires, the policy terminates, and no further coverage is provided. This means that if you outlive the policy term, you will need to renew or purchase a new policy to maintain coverage.
- No Cash Value Accumulation: Unlike permanent life insurance, term life insurance does not build up cash value. This means that you cannot access any accumulated funds during the policy term or withdraw them upon policy expiration.
Permanent Life Insurance
Permanent life insurance provides lifelong coverage, meaning it remains in effect as long as you pay your premiums. Unlike term life insurance, which has a limited duration, permanent life insurance offers coverage for your entire life. This makes it a suitable option for individuals seeking long-term financial security and protection for their loved ones.
Types of Permanent Life Insurance
Permanent life insurance comes in various forms, each with its unique features and benefits. Here are some of the most common types:
- Whole Life Insurance: This type of insurance offers fixed premiums and a guaranteed death benefit. It also builds cash value that grows at a predetermined rate, allowing you to borrow against it or withdraw funds.
- Universal Life Insurance: Universal life insurance provides flexible premiums and a death benefit that can be adjusted based on your needs. It also offers a cash value component that earns interest based on current market rates, giving you greater control over your policy’s growth.
- Variable Life Insurance: Variable life insurance allows you to invest your cash value in a range of sub-accounts, similar to mutual funds. This provides the potential for higher returns but also carries investment risk. Your death benefit may fluctuate depending on the performance of your chosen investments.
Cash Value Accumulation
Permanent life insurance policies accumulate cash value over time. This cash value represents a portion of your premium that is not used to cover the cost of insurance. It is invested and grows over time, providing you with a source of savings and potential tax benefits.
- Accessing Cash Value: You can access your cash value through withdrawals, loans, or policy surrender. Withdrawals are typically taxed as ordinary income, while loans are considered debt that you must repay with interest. Policy surrender involves cashing out your policy and receiving the accumulated cash value, but it may result in tax consequences and loss of coverage.
Advantages of Permanent Life Insurance
Permanent life insurance offers several advantages that make it attractive to many individuals.
- Lifelong Coverage: Permanent life insurance provides coverage for your entire life, ensuring your beneficiaries receive a death benefit regardless of when you pass away.
- Cash Value Growth: Permanent life insurance policies accumulate cash value that can grow over time, providing a source of savings and potential tax benefits. You can access this cash value for various financial needs, such as retirement planning, education expenses, or emergency funds.
- Potential Tax Benefits: The cash value growth in permanent life insurance policies is typically tax-deferred, meaning you won’t have to pay taxes on the earnings until you withdraw them. Additionally, death benefits received by your beneficiaries are generally tax-free.
Disadvantages of Permanent Life Insurance
While permanent life insurance offers several advantages, it also comes with some drawbacks.
- Higher Premiums: Permanent life insurance policies generally have higher premiums compared to term life insurance because they offer lifelong coverage and cash value accumulation. This can make them less affordable for individuals on a tight budget.
- Complexity: Permanent life insurance policies can be more complex than term life insurance, involving various features and options that may require careful consideration and understanding.
- Potential Investment Risk: Some types of permanent life insurance, such as variable life, involve investment risk. The value of your cash value may fluctuate depending on the performance of your chosen investments, potentially impacting your death benefit.
Cost Comparison
The cost of life insurance is a crucial factor in choosing the right policy. Term life insurance and permanent life insurance have distinct pricing structures, influenced by various factors. Understanding these differences is essential for making an informed decision.
Premium Costs
The premium for term life insurance is generally lower than for permanent life insurance. This is because term life insurance provides coverage for a specific period, typically 10, 20, or 30 years. If the insured dies within the term, the death benefit is paid out. However, if the insured outlives the term, the policy expires and no death benefit is paid. Permanent life insurance, on the other hand, provides lifetime coverage, meaning the death benefit is paid out whenever the insured dies, regardless of when that occurs.
- Term Life Insurance: Premiums are typically lower because the insurance company is only obligated to pay the death benefit during the specified term. The risk for the insurance company is limited, resulting in lower premiums.
- Permanent Life Insurance: Premiums are higher because the insurance company is obligated to pay the death benefit at any time, regardless of the insured’s age. This longer-term commitment carries a higher risk for the insurance company, leading to higher premiums.
Level Premium
Term life insurance typically features a level premium, meaning the premium remains constant throughout the policy term. This provides predictability and budgeting ease for policyholders.
A level premium for term life insurance means that the premium remains the same throughout the policy term, regardless of age or health changes.
Permanent life insurance premiums, however, are not always level. The premium may increase over time, depending on the type of permanent life insurance policy.
Premium Increases
Premium increases in permanent life insurance policies can occur for various reasons, including:
- Interest Rate Fluctuations: Some permanent life insurance policies, such as universal life insurance, have premiums linked to interest rates. If interest rates decline, premiums may increase to maintain the policy’s cash value.
- Changes in Mortality Rates: If mortality rates increase, the insurance company may need to charge higher premiums to cover the increased risk.
- Policy Expenses: Administrative and other policy expenses can contribute to premium increases over time.
Coverage Needs

Determining the appropriate amount of life insurance coverage is a crucial step in securing your family’s financial well-being. This decision involves a comprehensive assessment of your current financial obligations, the number of dependents you support, and your income level.
Financial Obligations
The amount of life insurance you need should be sufficient to cover your outstanding financial obligations in the event of your death. This includes:
- Mortgage or rent payments: Your life insurance policy should provide enough funds to pay off your mortgage or ensure continued rent payments for your family.
- Outstanding debts: Consider any loans, credit card debt, or other outstanding financial obligations that your family would need to repay.
- Education expenses: If you have children, your life insurance policy should provide funds to cover their future education costs.
- Other expenses: Include any other expenses that your family would need to cover, such as living expenses, medical bills, or funeral costs.
Dependents
The number and age of your dependents significantly influence your life insurance needs. A larger family with younger children will generally require more coverage than a smaller family with older, financially independent children.
Income Levels
Your income level plays a vital role in determining the amount of life insurance you need. A higher income generally translates to a greater need for life insurance coverage to ensure your family’s financial stability in your absence. For example, a high-income earner may require a larger life insurance policy to replace their lost income and support their family’s lifestyle.
Term Life Insurance and Permanent Life Insurance Coverage
Term life insurance provides coverage for a specific period, typically 10 to 30 years. It is generally more affordable than permanent life insurance and is ideal for individuals who need coverage for a limited time, such as during their working years when they have young children or a mortgage.
Permanent life insurance, on the other hand, provides lifelong coverage and accumulates cash value that can be borrowed against or withdrawn. It is a suitable option for individuals who need long-term coverage and want to build cash value for future needs.
Term life insurance is a cost-effective solution for temporary coverage needs, while permanent life insurance offers lifelong protection and a cash value component.
Investment Options
Permanent life insurance policies offer investment features, allowing policyholders to accumulate cash value that can be invested. This cash value grows over time, potentially providing tax-advantaged returns and a source of funds for various financial needs.
Cash Value Investment Options
Permanent life insurance policies typically offer a range of investment options for the cash value component. These options vary depending on the insurer and the specific policy.
- Fixed Interest Accounts: These accounts provide a guaranteed interest rate, offering stability and predictable returns. The interest rate is typically fixed for a specific period, after which it may be adjusted based on market conditions. These accounts are ideal for those seeking a low-risk investment option with a guaranteed return.
- Variable Accounts: These accounts allow policyholders to invest in a range of sub-accounts, including mutual funds, stocks, and bonds. The value of these accounts fluctuates with market performance, offering potential for higher returns but also greater risk. Variable accounts are suitable for individuals with a higher risk tolerance and a longer investment horizon.
- Indexed Accounts: These accounts link the cash value growth to the performance of a specific market index, such as the S&P 500. While they offer potential for higher returns, they typically have a cap on the growth rate. Indexed accounts provide a balance between potential growth and some level of protection from market downturns.
Cash Value Growth and Potential Returns
Cash value grows over time through interest, dividends, and investment gains. The growth rate depends on the chosen investment options and the overall performance of the underlying investments. For example, a policy with a fixed interest account may earn a guaranteed 3% annual return, while a variable account invested in a stock mutual fund may experience higher or lower returns based on market fluctuations.
Cash value growth is not guaranteed and may fluctuate based on market performance and investment choices.
Investment Risks Associated with Different Permanent Life Insurance Types
The investment risks associated with permanent life insurance policies vary depending on the specific type of policy and the investment options selected.
- Whole Life Insurance: Whole life insurance policies typically offer a fixed interest rate on the cash value, providing a guaranteed return. However, this return may be lower than the potential returns offered by other investment options, such as variable accounts. Whole life insurance policies are generally considered less risky than other types of permanent life insurance, as the cash value growth is not tied to market performance.
- Universal Life Insurance: Universal life insurance policies provide more flexibility in investment options, allowing policyholders to choose from a range of sub-accounts. However, this flexibility also comes with greater risk, as the cash value growth is directly tied to the performance of the chosen investments. If the investments perform poorly, the cash value may decline, potentially impacting the death benefit and the policy’s overall value.
- Variable Life Insurance: Variable life insurance policies offer the most flexibility in investment options, allowing policyholders to invest in a wide range of securities, including stocks, bonds, and mutual funds. This flexibility also comes with the highest risk, as the cash value growth is entirely dependent on market performance. Variable life insurance policies are suitable for individuals with a high risk tolerance and a long investment horizon.
Tax Considerations
Life insurance policies, whether term or permanent, come with specific tax implications. Understanding these tax aspects is crucial for making informed decisions about your insurance coverage. This section will delve into the taxability of death benefits and cash value withdrawals for both term and permanent life insurance policies.
Taxability of Death Benefits
Death benefits received from life insurance policies are generally tax-free. This means that the beneficiary receiving the death benefit does not have to pay income taxes on the proceeds. This exemption from income tax applies to both term and permanent life insurance policies.
The tax-free nature of death benefits makes life insurance a valuable tool for estate planning, as it allows for tax-efficient wealth transfer to beneficiaries.
Taxability of Cash Value Withdrawals
Permanent life insurance policies accumulate cash value, which can be accessed by the policyholder through withdrawals or loans. The tax implications of cash value withdrawals depend on the type of permanent life insurance policy and the method of withdrawal.
Taxation of Cash Value Withdrawals: Traditional Permanent Life Insurance
In traditional permanent life insurance policies, withdrawals from the cash value are generally considered taxable income. This is because the cash value growth is considered to be a tax-deferred investment, and withdrawals are treated as a return of principal first, followed by taxable earnings.
For example, if you withdraw $10,000 from a cash value policy with $5,000 in accumulated earnings, the first $5,000 would be considered a tax-free return of principal, while the remaining $5,000 would be taxed as ordinary income.
Taxation of Cash Value Withdrawals: Roth Permanent Life Insurance
Roth permanent life insurance policies, unlike traditional policies, allow for tax-free withdrawals of cash value. This is because premiums are paid with after-tax dollars, and the growth of the cash value is also tax-free.
Roth permanent life insurance offers a tax-advantaged way to accumulate wealth and access funds tax-free during retirement.
Tax Advantages of Permanent Life Insurance
Certain types of permanent life insurance policies, such as indexed universal life insurance (IUL), offer tax advantages related to investment growth.
Tax Advantages of Indexed Universal Life Insurance
IUL policies allow the cash value to grow based on the performance of a specific index, such as the S&P 500. The earnings on the cash value are tax-deferred, and withdrawals are generally treated as tax-free returns of principal first, followed by taxable earnings.
IUL policies can provide a tax-efficient way to invest in the stock market and potentially generate higher returns than traditional permanent life insurance policies.
Suitability
Choosing between term life insurance and permanent life insurance depends on your individual needs, financial situation, and life stage. Both types of insurance offer unique benefits, but understanding their suitability for different circumstances is crucial for making an informed decision.
Comparing Key Features
The following table highlights the key features of term life insurance and permanent life insurance:
| Feature | Term Life Insurance | Permanent Life Insurance |
|——————|———————|————————–|
| Coverage | Death benefit only | Death benefit and cash value |
| Term | Temporary, typically 10-30 years | Lifetime |
| Premiums | Typically lower | Typically higher |
| Cash Value | None | Accumulates over time |
| Investment Options | None | May offer investment options |
| Flexibility | Less flexible | More flexible |
Suitability for Different Life Stages and Financial Situations
- Young Families: Term life insurance is often the most suitable option for young families with a limited budget. It provides a substantial death benefit at an affordable premium, ensuring financial security for dependents in case of the policyholder’s untimely death.
- Individuals with a High Debt Burden: Term life insurance can be an effective way to protect loved ones from financial hardship caused by outstanding debts, such as mortgages or loans.
- Individuals with a Limited Budget: Term life insurance offers the most affordable coverage, making it a suitable option for individuals with limited financial resources.
- Individuals with a Long-Term Financial Planning Horizon: Permanent life insurance, with its lifetime coverage and cash value accumulation, can be a valuable tool for long-term financial planning. The cash value can be used for various purposes, such as retirement planning, education expenses, or unexpected financial needs.
- High-Net-Worth Individuals: Permanent life insurance can be a suitable option for high-net-worth individuals seeking estate planning strategies, tax advantages, and long-term wealth preservation.
Examples of Scenarios
- Scenario 1: A young couple with a newborn baby and a mortgage might choose term life insurance to provide financial security for their family in case of the untimely death of either parent. The affordable premiums of term life insurance allow them to obtain significant coverage without straining their budget.
- Scenario 2: A self-employed individual with a large business loan might choose term life insurance to protect their business from financial hardship in case of their death. The death benefit would help cover the outstanding loan balance, ensuring the business’s continued operation.
- Scenario 3: A successful entrepreneur with a substantial net worth might choose permanent life insurance to create a legacy for their family, minimize estate taxes, and provide long-term financial security. The cash value accumulation feature of permanent life insurance can also be used for estate planning purposes and tax-advantaged investment opportunities.
Choosing the Right Policy
Selecting the right life insurance policy is a crucial decision that requires careful consideration of your individual circumstances, financial goals, and risk tolerance. It is essential to approach this process with a clear understanding of your needs and objectives.
Identifying Key Questions
To ensure you make an informed decision, it is essential to ask yourself the following questions:
- What is your primary reason for purchasing life insurance?
- What are your financial goals and objectives?
- What is your risk tolerance?
- What is your budget for life insurance premiums?
- What is your health status?
- What are your dependents’ needs?
- What is your age and expected lifespan?
- What is your income and financial stability?
- Do you have any existing debt?
- Do you have any other assets or investments?
- What are your long-term financial plans?
Conclusion
Choosing between term life insurance and permanent life insurance is a significant financial decision that requires careful consideration. Both types of insurance offer unique benefits and drawbacks, and the most appropriate choice depends on individual circumstances and financial goals.
This article has explored the key differences between term and permanent life insurance, highlighting the advantages and disadvantages of each type. It has also provided insights into factors such as cost, coverage needs, investment options, tax considerations, and suitability.
Factors to Consider
The decision of whether to choose term or permanent life insurance involves weighing various factors, including:
- Financial Goals: Term life insurance is typically more affordable, making it a suitable option for individuals seeking temporary coverage, such as during periods of high financial responsibility. Permanent life insurance, on the other hand, provides lifelong coverage and offers investment opportunities, making it a more suitable choice for those seeking long-term financial security and wealth accumulation.
- Coverage Needs: The amount of coverage required depends on individual circumstances, such as dependents, outstanding debts, and desired legacy. Term life insurance offers high coverage amounts at a lower cost, while permanent life insurance provides a lower death benefit but offers additional benefits such as cash value accumulation.
- Budget: Term life insurance is generally more affordable than permanent life insurance, making it an attractive option for budget-conscious individuals. Permanent life insurance premiums are typically higher due to the inclusion of investment components.
- Investment Options: Permanent life insurance policies often include cash value components that allow policyholders to invest and grow their funds over time. This can be a valuable feature for individuals seeking to build wealth or supplement retirement income.
- Tax Considerations: Both term and permanent life insurance policies offer tax advantages, but the specific benefits can vary depending on the type of policy and the individual’s financial situation. It is essential to consult with a financial advisor to understand the tax implications of each type of insurance.
Importance of Professional Advice
It is crucial to consult with a qualified financial advisor to determine the most appropriate type of life insurance for your individual needs. A financial advisor can help you assess your financial goals, risk tolerance, and coverage requirements, and provide personalized recommendations based on your specific circumstances.
Closure
Ultimately, the choice between term life insurance and permanent life insurance depends on your individual circumstances, financial goals, and risk tolerance. While term life insurance offers affordable temporary coverage, permanent life insurance provides lifelong protection and potential investment opportunities. It’s crucial to carefully consider your needs and consult with a financial advisor to determine the most suitable type of insurance for your situation.